Published November 28, 2020 on Wrong Kind of Green
Part three. This is the final segment of a three-part investigative series. [Part 1] [Part 2]
Artificial intelligence, Automation – & Cyberwarfare
Announced at the Global Inclusive Growth Summit on October 21, 2019, the Imperative 21 RESET campaign was launched to the public on September 13, 2020. A front campaign of The Business Roundtable, the six founding coalition partners are The B Team, JUST Capital, B Lab, Chief Executives for Corporate Purpose (CECP), Inclusive Capitalism and Conscious Capitalism. [Further reading: The Business Roundtable/CURT a Systematic Destruction of Labor]
“It’s an unprecedented coalition of business networks that have come together to raise our ambition. Not just to help our individual CEOs succeed, we’ll do that for sure. But to actually bring their voices together to help shift culture. So that the pushback on the BRT [Business Roundtable] from different business publications or other people within the business community lessens. So there’s less of a headwind culturally for this type of leadership.”
— Jay Coen Gilbert, co-founder of B Lab and B Corporations [Source]
rtificial Intelligence (AI) is described as, “systems that combine sophisticated hardware and software with elaborate databases and knowledge-based processing models to demonstrate characteristics of effective human decision making.” [Source] The World Economic Forum recognizes AI as “the engine of the Fourth Industrial Revolution”. [Source] AI as applied/ utilized by social media platforms is trained with an objective and exploitative function: target users with ads for maximum ad revenue, by highlighting the newsfeed ensuring users remain on the platform for as many hours, minutes and seconds as possible. This function is highlighted by The Social Dilemma, while, ultimately, the sole function of every corporation, that of increasing revenues and maximizing profits – ad infinitum, is kept opaque.
Any technology that has power can be corrupted. In this respect, AI is perhaps the most dangerous. Hacking (PC, mobiles, viruses) is accomplished by injecting code – code that can be then detected. Deep learning, referred to as artificial intelligence, is a giant array of numbers. The AI models are self-modifying on a continuous basis, thus, it is unknown how hacking AI can – or will – be aptly detected. [Source: October 5, 2018, The Artificial Intelligence Race and the New World, Order, Council on Foreign Relations – The Malcolm and Carolyn Wiener Lecture on Science and Technology]. “Imagine tens of millions of numbers in the deep learning algorithm that’s updating itself anyway, because it’s getting more data, retraining itself. Some bad people just tweak a few numbers and all of a sudden, it might be out of control.” [Source] Meaning, for example, a hacker may succeed in turning autonomous vehicles into autonomous weapons that kill people en masse. Imagine fully autonomous nuclear weapons or autonomous nuclear power plants, the hacking of which – or malfunction of – could result in the annihilation of an entire nation, or the entire planet.
Here again, it is more important what both The Social Dilemma and the Center for Humane Technology do not divulge, rather than what they do. The Fourth Industrial Revolution cannot come into fruition without the 5G infrastructure that will run the Internet of Things. “Smart” cities must be understood within the context of global policing and the military industrial complex. Cybersecurity will be the battle space of the 21st century.
“The potential for nuclear escalation in a conventional conflict with autonomous systems is compounded by the way that autonomous systems could enable adopters to fight faster than those operating non-autonomous systems do at present… A military force that is heavily invested in AI could essentially enable faster operations by autonomous systems relative to remotely-piloted or inhabited systems. Some Chinese scholars have hypothesized that this trend could result in a “battlefield singularity,” in which the pace of action on the battlefield eclipses the speed of human decision-making.” [Source]
Remarks to the Association of the U.S. Army Annual Convention, October 4, 2016, as Delivered by Deputy Secretary of Defense Bob Work, Washington, D.C.:
Q: “You didn’t mention about autonomous systems. In light of the third off-set strategy, what is your thinking about letting in the future autonomous systems make lethality decisions without a human in the loop?”
A: “I purposely didn’t talk a lot about the technology behind the third off-set because in a audience like this, you get that the most important thing is the operational concepts and the organizational constructs that employ that technology. But let me state this, state it this way. There will be some instances where operations are happening at machine speeds and we will have to rely upon A.I. and autonomy to actually fight.” [Source]
Automation bias is when humans effectively surrender their judgment to machines:
“Of particular concern in the design of intelligent decision support systems is the human tendency toward automation bias, which occurs when a human decision maker disregards or does not search for contradictory information in light of a computer-generated solution which is accepted as correct. Operators are likely to turn over decision processes to automation as much as possible due to a cognitive conservation phenomenon and teams of people, as well as individuals, are susceptible to automation bias.” [Further reading: Automation Bias in Intelligent Time Critical Decision Support System, AIAA 1st Intelligent Systems Technical Conference, 20-22 September, 2004]
To fully comprehend this risk, a cognitive conservation phenomenon, one must contemplate the Stanislav Petrov incident. In 1983, the satellite-based Soviet Oko nuclear early warning system detected that an intercontinental ballistic nuclear missile had been launched by the United States. The automated system reported, with the “highest” confidence, that a U.S. missile strike was underway. Lieutenant Colonel Stanislav Petrov, on duty, was responsible for alerting his Soviet superiors of the attack. The siren sounded while a large screen instructed “launch” in bold red letters. The siren continued to sound as the computer identified a secondary, third, fourth and fifth missile launch, changing its instruction from “launch” to “missile strike.” Doubting the accuracy of the computer system, Petrov did not react with counter missiles, later explaining “I had a funny feeling in my gut”. He resisted falling victim to automation bias and reported a system malfunction to his superiors, rather than responding with a counter strike. Rather than launching a nuclear war. Rather than ceding his own judgment to a machine. If this had of been a fully autonomous system, as desired by global technocrats, the counter strike would have been automatic, likely unimpeded by human intervention.
[In his own words: Ex-Soviet officer Stanislav Petrov reported a possible 1983 US missile launch as a false alarm: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L7EmLf4Xlq0]
In 2003, U.S. army investigators found that automation bias was pervasive within the “Patriot community”, which espoused a culture of “trusting the system without question”. “Patriot operators” exhibited an “unwarranted and uncritical trust in automation. In essence, control responsibility [was] ceded to the machine.” [Source]
“The more a country fears that, in a world without using autonomous systems, its ability to retaliate to a nuclear strike would be at risk, the more attractive autonomous systems may appear.”
— A Stable Nuclear Future? The Impact of Autonomous Systems and Artificial Intelligence, December 2019
6G promises increased bio-cybernetic identity (identity critical service architecture, sensing based machine learning, distribution of trust) and cyber security. Now consider activity that is deemed criminal by larger society. Rather than obtaining physical keys and/or passwords to acquire access, one will require biometric access. That is, heads (face recognition), eyes (retina scanning), and/or hands.
The AI arms race between China and the US is already well underway (with China having launched its blockchain in April 2020, for global commercial use). The idea that regulation and safeguards cab be applied to AI, ensuring both privacy and data are protected, borders on the edge of a collective psychosis. Such are the lies we tell ourselves in order to sleep at night.
“The Fourth Industrial Revolution and Its Impact on Occupational Health and Safety, Worker’s Compensation and Labor Conditions”, September, 2019:
“In FIR [fourth industrial revolution], nonstandard employment will be common. As a result, it is difficult to receive OHS services and compensation. Excessive trust in new technologies can lead to large-scale or new forms of accidents. Global business networks will cause destruction of workers’ biorhythms, some cancers, overwork, and task complexity. The social disconnection because of an independent work will be a risk for worker’s mental health. The union bonds will weaken, and it will be difficult to apply standardized OHS regulations to multinational enterprises.”
The Unfinished Network includes Ashoka, Aspen Institute, Ford Foundation, For Freedoms, Georgetown University, Imperative 21, the Max Steinbeck Charitable Trust, McCourt, Mil M2, PolicyLink, and The Shed.
Tristan Harris, co-founder, The Center for Humane Technology. ” By tapping into the power of communities, creative media and new technology, Unfinished connects thought leaders, culture shapers, policy makers and innovators to provoke ideas, elevate unheard voices and pursue collaborations for greater impact. Unfinished is headquartered in New York City and its network partners span the world.” [Source]
Rather than a collective demand from the citizenry to terminate the foray into unchartered territory, fully recognized as extremely dangerous and high-risk by those pushing the technologies forward, a discourse is manufactured. Fearing global opposition, the public is safely re-routed and encouraged to, “demand” a future that respects “humane technology”, with adherence to the precautionary principle, kept both out of sight and out of mind. In public relations, this is referred to as “crisis management”. That is, getting ahead of a crisis – monitoring, controlling and shaping public perception at all times. The wish for a “humane technology” is one that will not come true.
Smash the Smartphone
As of July 2020, there were over 290 million Facebook users in India. With 2.6 billion monthly active users, 98% of active Facebook users access the platform via mobile, with over 90% of Facebook’s ad revenues coming in via the device. [Source] Mobile advertising has become the lion’s share of Facebook’s total advertising revenue in recent years, growing from a mere 11% in 2012 to a whopping 92 percent in 2018. This translates to over 50 billion U.S. dollars in annual mobile ad revenues.” [Source]
In the fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2020, 98% of Facebook’s revenue was generated through advertising. The social network’s global mobile sponsored stories account for approximately half of this advertising revenue – while approximately 50% of Apple’s revenue came from a single device, the iPhone. [Source] [Source]
Facebook revenues at a glance:
-Approximately 2.7 billion monthly active users
-98% of Facebook users access the platform via mobile
-Over 90% of ad revenues are earned via mobile
-98% of revenue was generated through advertising in 2020
-The network’s global mobile sponsored stories account for approximately half of the advertising revenue
Harris is quick to point out that, “The solution isn’t abstinence, the solution is connection.” [Thrive Global interview with Tristan Harris, April 9, 2017] Yet, nothing could be further from the truth. The solution isn’t connection – via the mobile, the solution is abstinence.
More than just abstaining, the solution has to be for everyone who owns a smartphone to trash it – never looking back. It is fact that “the fourth industrial revolution [“Great Reset”] flows through a mobile”. [Source] The smartphone is the conduit. Although the smartphone is the key to unlocking future nightmares, it’s also very much a double-edged sword. In the same way it serves to uphold the Fourth Industrial Revolution architecture, unveiled to the public as the “Great Reset”, without the smartphone, this very foundation would collapse like a house of cards. The truth is, if no one purchased smartphones, they would give them away in cereal boxes.
But this window is closing.
In the 2030 6G era, “smart phones are likely to be replaced by pervasive XR experiences through lightweight glasses”. [“Virtual (VR)11, 12 augmented (AR)13, and mixed reality (MR) technologies are merging into XR, which encompasses wearable displays and interaction mechanisms that create and maintain perceptual illusions.”] [Source: 6G Research Visions 1, September 2019]
“In the most advanced countries, today’s digital consumers (using PCs and smartphones) will likely become tomorrow’s augmented customers, adopting emerging technologies such as AI (via smart speakers) and immersive reality.”
— The Mobile Economy 2019, GSMA Intelligence, [Source]
It is critical to note that a vast majority of internet users (91%) now use mobile devices exclusively to go online. [Source] This is significant for a couple of reasons. First of all, this sheds much light on the ever devolving critical thinking skills by those in the West most impacted and captured by the mobile phone. Detailed information, required for in-depth critical thinking, is largely impossible to decipher and analyze using a tiny mobile device.
One should know full well by now that the success of corporate products with names preceded by the word smart – are hinged on the hope that the “consumer”, or targeted demographic, is vacuous. Anything “smart” serves capital first and foremost. Humans have survived successfully for millennia without mobiles. All we require for our survival is healthy food, clean water, clean sanitation, and shelter. And as social animals, we seek physical community, companionship, joy, and love.
The Internet Society, the United Nations & the World Economic Forum
On September 25, 2018, the Internet Society (ISOC), situated in the US and Switzerland, partnered with Facebook to expand internet connectivity in Africa. [Source] Since then, IXP [internet exchange points] workshops have been held in Morocco, Nigeria, Burkina Faso, Zimbabwe, Togo, Lesotho, Burundi, Mauritius, Guinea, Benin and Chad. [Source] Internet Society partners include Access Now (a tentacle of Avaaz) [1] and Center for Democracy & Technology. The Board of Directors, serving as the Center for Democracy & Technology’s governing body, includes Julie Brill,Corporate Vice President & Deputy General Counsel, Microsoft and Philippa Scarlett, Former Deputy Intellectual Property Enforcement Coordinator, The White House. Advisory council members include affiliates of the Charles Koch Institute, RAND Corporation, Walmart, Facebook, Twentieth Century Fox, Amazon, MasterCard and Verizon. [Full list]
The Center was founded in 1992 by internet pioneers Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn. Widely referred to the “Fathers of the Internet,” Cerf and Kahn co-designed the TCP/IP protocols and the architecture of the Internet”, with both having held executive positions at DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency). Cerf serves as Vice President and Chief Internet Evangelist for Google since October 2005 with a focus on the future of tech in areas such as artificial intelligence. Since 2010, Cerf has served as a Commissioner for the UN Broadband Commission for Digital Development while Kahn serves as chairman, CEO and president of the Corporation for National Research Initiatives. Cerf also serves as member of the UN High Level Panel on Digital Cooperation, and was present at the launch of the Panel’s first report, “The Age of Digital Interdependence” released on June 10, 2019. [Source]
The Internet Society “is leading and facilitating the multi-round meetings for the Stakeholders Dialogue to collect, compile, and submit the inputs of the worldwide professionals and experts for future governance of the Internet.”
“I used to think it was a funny joke to say [that] the thing I worry about is 100,000 refrigerators attacking [the] Bank of America. That’s not a joke anymore.”
— Vint Cerf, 2020
In January 2019, the UN High Level Panel on Digital Cooperation convened. Created at the behest of the UN Secretary-General the year prior, such a high-level panel is rare, with only around 20 having been convened in the UN’s 70-year history. The 20-strong panel is co-chaired by Jack Ma, founder of Aliba, member of the Foundation Board of the World Economic Forum, Foundation Board of World Economic Forum Global Shapers Community, Member of the Board of Trustees, World Economic Forum, Global Board of Directors, The Nature Conservancy, co-founder and board of the Breakthrough Energy Ventures (with a focus on nuclear), and Melinda Gates:
“In his appeal to a UN panel of experts led by philanthropist Melinda Gates and Alibaba founder Jack Ma, Secretary-General António Guterres called on its members to reflect on the risks and benefits of our digital age – the so-called Fourth Industrial Revolution. ‘We need new thinking and innovative ideas to harness the benefits and manage the risks of this digital age,’ he said via video-link, while urging the High-level Panel on Digital Cooperation to reflect on how technology could accelerate the 2030 Agenda on sustainable development.”
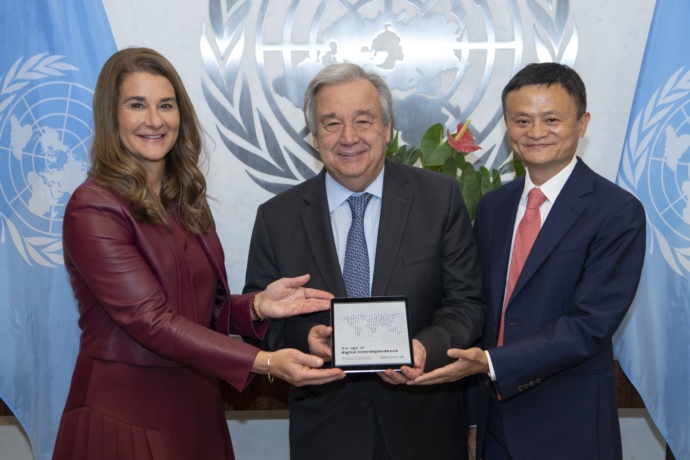

Handover of the Report of the High-level Panel on Digital Cooperation to Secretary General Antonio Guterres.
Serving the 20-throng panel is “His Excellency” Mohammad Al Gergawi, the United Arab Emirates’ Minister of Cabinet Affairs and The Future, Chairman of the UAE Council for the Fourth Industrial Revolution; Fadi Chehadé, partner at ABRY in Boston, a private equity firm, and advisory board member with the World Economic Forum’s Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution; Dr. Cathy Mulligan is a Visiting Research Fellow at Imperial College Centre for Cryptocurrency Research and Engineering, a Senior Research Associate at University College London in Blockchain and a Fellow and Expert Member of the World Economic Forum’s Blockchain Council; Marina Kolesnik, co-founder of internet ventures and Young Global Leader at the World Economic Forum. [Full list]
“Growing opportunities created by the application of digital technologies are paralleled by stark abuses and unintended consequences. Digital dividends co-exist with digital divides. And, as technological change has accelerated, the mechanisms for cooperation and governance of this landscape have failed to keep pace.”
— June 10, 2019, “The Age of Digital Interdependence” — Report of the High-level Panel on Digital Cooperation
At this same time, the Global Commission on the Stability of Cyberspace meeting took place where a more candid, somber and cautionary tone presided, with the UN’s Fabrizio Hochschild, Assistant Secretary-General for Strategic Coordination, remarking:
“After years of unbridled optimism – justified optimism – surrounding the development of digital technologies of cyberspace, we now have come to the sober realization that those positive developments carry downsides.
We’re at the point of asking ourselves, will emerging technologies contribute to peace overall or will they undermine it? Will they generally further access to sustainable development or will they further inequality? Will they facilitate respect for human rights or will they provide new tools to those who wish to contain or violate the realization of human rights?
Some 30 States have the capacity to defend themselves and those capacities are daily being built up. But where does that leave the other 163 countries that don’t have such a capacity, or the financial means, or political means to defend themselves?” [Source]
The high-level panel chaired by Gates and Ma has proposed three models: a Digital Commons Architecture (DCA), a Distributed Co-Governance Architecture (CoGov) (voluntary solutions rather than legal instruments), and a reformed Internet Governance Forum (IGF+) (enhances and extends the IGF established in 2005). The proposed “Digital Commons Architecture” would aim to synergise efforts by governments, civil society and businesses to ensure digital technologies promote the SDGs under the pretext of addressing risks of social harm, in addition to developing certification schemes for high-risk technologies such as “autonomous intelligent systems” operated by artificial intelligence (AI). [Source: The Age of Digital Interdependence Report of the UN Secretary-General’s High-level Panel on Digital Cooperation, June 10, 2019] AI and cybersecurity certification schemes represent another lucrative emerging market, with billion dollar certification schemes having served to greenwash, thus secure, the continued plunder of the planet since the early 1990s. Such schemes can serve as a key apparatus in providing and/or maintaining the required social license to operate. [The EU cybersecurity certification framework]
“Think of personal data as the digital record of “everything a person makes and does online and in the world.”
– Personal Data: The Emergence of a New Asset Class, World Economic Forum, January 2011
The panel also placed an emphasis on Blockchain. In 2017, the United Nation’s World Food Programme (WFP) piloted the “Building Blocks” project in Sindh, Pakistan, employing the Ethereum Blockchain to distribute aid and test biometrics. This program falls under SDG #2, “zero hunger” (an emerging market in the poverty economy), and #17, partnerships. Following the test-run with 100 citizens, the second phase was then rolled out in Jordan at two refugee camps. This phase commenced with 10,000 refugees, then scaled to 100,000. The next phase is to increase the refugee participants to 500,000. Whereas in the Pakistan pilot, smartphones were used for the transactions, the Jordan project switched over to a private blockchain – with eye-scanning hardware to confirm the identity of those receiving aid. Refugees received a debit in the form of a “virtual wallet” – to be spent exclusively within the giant WFP-contracted supermarkets (“hypermarkets”). Checkout would be authorized via the IrisGuard “EyePay”.
“Syrian refugees receive foodstuff through the iris scan service launched by the World Food Program at Tazweed centre in the Al-Zaatari refugee camp, in Mafraq, Jordan, near the border with Syria, November 23, 2016.” Reuters/Muhammad Hamed [Source]
The first major testing ground, the Zaatari Refugee Camp, encloses 80,000 displaced citizens (150,000 in 2013) – with nearly 60% of the displaced (55.8%, January 2020) under 17 years of age. Overseen by 44-45 organizations such as USAID, UKAID and NGOs including Oxfam, ACTED and IRD, Zaatari [2] is now referred to as one of the many growing permanent settlements: thousands of acres of land, holding tens of thousands of displaced people, enclosed within barbed wire fence perimeters, contained by police and military. Today, these open prisons, created by imperialist aggression against targeted sovereign states, are being redesigned and redefined as “liveable cities” and “smart cities. In 2014, it was reported that Zaatari costs approx. a half million dollars per day to run (with half a million pieces of bread and 4.2m litres of water distributed daily.) The second testing ground, the Azraq Camp (holds roughly 40,000 displaced peoples in 2020) would result in 100,000 blockchain transactions (totaling 1 million dollars) and retina scans. The WFP has a record of every transaction – with data as a new asset class. These transactions and iris scans will remain on the blockchains utilized (both public and private) – for eternity. In this video overview, the imperial destabilization and attempted annihilation of Syria is framed as a “civil war”, while the data harvesting itself is framed as privilege. Building Blocks is growing and set to expand.[Source][Source] [Source][Source] Jordan remains the second largest refugee host per capita worldwide with 650,000 – 750,000 displaced peoples. [Source]
The World Food Programme has three foundation partnerships: the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Children’s Investment Fund Foundation, and the Rockefeller Foundation. Corporate supporters include PepsiCo, MasterCard, and Unilever. [Corporate Partners]
“Personal data is the new oil of the Internet and the new currency of the digital world.”
— Meglena Kuneva, European Consumer Commissioner, March 2009, Personal Data
On June 11, 2020, UN Secretary-General Guterres announced the issuance of his report, Roadmap for Digital Cooperation, “on the impact of rapid technological change on the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals and targets”. High Level Speakers included: Sheikh Hamdan bin Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, Crown Prince of Dubai, Klaus Schwab, Executive Chairman, World Economic Forum, Ajay Banga, Chief Executive Officer, MasterCard, Nick Read, Chief Executive Officer, Vodafone Group, Fekitamoeloa Katoa ‘Utolkamanu, High Representative for the Least Developed Countries, Landlocked Developing Countries, and Small Island Developing States (UN-OHRLLS), “Baroness” Joanna Shields OBE, Chief Executive Officer, BenevolentAI, and Andrew Sullivan, President and Chief Executive Officer, Internet Society. [Source]
June 11, 2020, The State of the Digital World Today / Roadmap for Digital Cooperation, Klaus Schwab:
“Since the onset of Corona Virus, internet usage has increased by 70%, the use of communication apps has increased by 300%, and virtual collaboration tools by 600 percent. And some video streaming services have grown twenty fold.”
Schwab goes on to point out that this increase is only true for those connected to the internet. And that 30 years after the invention of the world wide web (1989) by Timothy John Berners-Lee, global internet users comprise just 53% of the world population. To accelerate the goal of internet access and consumption by every human being on Earth, the World Economic Forum has developed a joint action plan with the ITU, the World Bank, GSMA and industry partners. The plan seeks immediate acceleration of private public partnerships in 170 countries with a focus on digital infrastructure, user expansion, digital identity and digital payment systems and currencies. Schwab: “This fast-track partnership is deeply encouraging. A number of our partners have highlighted that we have made more progress in the last four months than in the last ten years.” [June 10, 2020]
“It is clear so the COVID-19 crisis is a watershed moment for digital infrastructure and services. Digital is the fabric of our post-covid lives. We will continue to rely on technology more and more. Unless we rapidly tackle the challenge to bring high quality universal internet access to all we will not be able to build inclusive economies or achieve our system.”
— World Economic Forum founder and CEO Klaus Schwab, June 10, 2020
Data Centers: A Hyperscale Tsunami of Renewable Energy Consumption is Underway
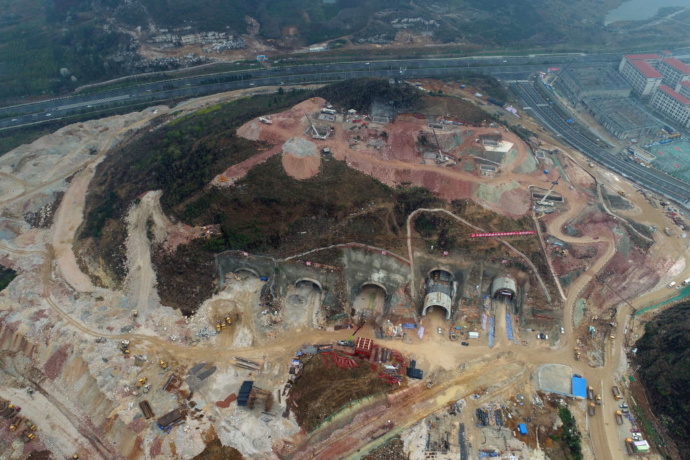

ANSHUN, CHINA – MARCH 13: Aerial view of Tencent’s biggest data center under construction in the mountainous area of the hinterland on March 13, 2018 in Anshun, Guizhou Province of China. As Tencent’s chairman Pony Ma Huateng referred in a media briefing in Beijing, his firm will continue to mine vast amounts of data to bolster a number of businesses including its own. (Photo by VCG/VCG via Getty Images)
“It has recently been discovered that data-intensive algorithms, such as at-scale machine learning training algorithms, are much more energy-intensive than was previously assumed.”
— The Hyperconnected World of 2030–2040, 2019 [Source]
“The international data corporation estimates that 152,000 new devices will be connecting to the internet every minute by 2025.”
“This will become completely unsustainable by 2040.”
— Anders Andrae, Senior Expert of Energy Efficiency, Emission Reduction, Sustainability and Life Cycle Assessment, Huawei Technologies, Sweden
Disconnected from the natural world, Western academia, sciences et al., continue to assign names to technology belonging to the very things being lost or systematically destroyed: “walled garden” (“a closed ecosystem in which all the operations are controlled by the ecosystem operator” i.e. Facebook and Google), “walled gardens of things” (constraint), “spiderweb of things” (transformation), “asteroid belt of things” (collapse), islands of things (growth), data center server “farms”, the internet and digital “ecosystems”, “apple”, Amazon, the “cloud”, “pollinators”. The list is endless.
“Behind the peaceful image of a white cumulus is a less poetic reality, that of data centres composed of thousands of servers that not only need plenty of energy to run, back up and store your files, but also air conditioning, 24 hours a day.”
— What Colour is the Cloud, June 21, 2019
The Social Dilemma, the Center for Humane Technology, and society at large, may speak of climate change, yet what is not addressed, in addition to militarism being a key driver of climate change, is the growing energy demand of information communications technology (ICT) which includes traditional data centers (server farms), network services, and hyperscale data centers. There is growing alarm over the energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions belonging to the exponential growth of the ICT industry. Of particular concern are the hyperscale data centers which are owned and operated by corporations Microsoft, Google, and Apple, etc. [“Hyperscale refers to the capability of an IT [information technology] system or architecture to scale exponentially and rapidly to respond to demand that is increasingly heavily.”][Source] There are now over 8 million data centers littering the planet, with 541 hyper scale data centers worldwide. At present, there are currently 176 more hyper scale data centers in development.
In 2017, data superseded oil, becoming the world’s most valuable commodity.
Often described as the “cloud” – successfully conjuring up a comforting perception that nothing exists beyond your device or laptop) – servers exist in real-world data centres. Information technology spending on data center systems worldwide in 2020 alone is estimated at USD 208 billion. [Source] On January, 15, 2020, Technavio released a report stating “hyperscalers” have invested approximately USD 200 billion in capacity expansion and opening of new data centers. For just a moment, contemplate the fact that those who promise an illusory “stakeholder capitalism” will spend billions to house data, while the subjugated and vulnerable remain homeless.
“We are using an immense amount of energy to drive this data revolution. It has real implications for our climate.”
— Jane Kearns, environment and technology expert, MaRS Discovery District, Toronto
The sheer magnitude and size of hyperscale data centers place enormous power demands upon global energy resources. Cisco estimates that by 2021, traffic within hyperscale data centers will have quadrupled, with hyperscale data centers accounting for approx. 55% of all data center traffic. [Source] At the local level, hyperscale data centres embody colossal electricity demand loads, adding pressure to electricity grids which are often already operating under duress. This is especially true for smaller or impoverished countries. Ireland is forecasting that 30% of their entire national grid will be earmarked for data center power consumption by 2028. One only needs to reflect upon the sheer enormity of these facilities proliferating the globe, to recognize the dire ecological impacts and consequences that lie ahead – upon an already plundered and decimated landscape and biosphere.
To ignore the ecological impact behind the exponential growth of ICT (information and communications technology), infrastructure, paramount for the Fourth Industrial Revolution to materialize, is in itself, a deliberate sleight of hand. A hypocritical genre of climate denialism practised and perfected by self-identifying liberals and progressives. At a moment’s notice, this faux left can be assembled on cue by those that preside over the non-profit industrial complex.
2017: Construction on the USD 1 billion 970,000-square-foot hyperscale Facebook data center. The 328-acre site became operational in 2019. At present, Facebook has 12 hyperscale data centers, nine in the U.S. and three in international markets amounting to nearly 15 million square feet of data center space completed or under construction, with several million more feet in the planning stages. [Source]
ICT (Information and Communications Technology)
Today the ICT industry represents the largest growing consumer of energy on the planet, with greenhouse gas emissions on par, or, more likely, far in excess of aviation. Depending on scope, in 2020 ICT accounts for up to 8% of the total global electricity. [Source] At the current rate of growth, approximately 9% each year (2018), the total electricity consumption of ICTs is projected to require 20% of the world’s electricity by 2025, and 30% all energy produced by 2030. [Source]
As concerns over data center energy consumption mount, obtaining the required data in order to ascertain the level of ecological damage resulting from the data centers becomes even more difficult. As criticisms of the industry grow, the global energy demands by data centers are being deliberately skewed downwards. Downward estimates are able to withstand scrutiny, due to the simple fact that there are no nationally reported statistics for data centers – and no global records. In a global corporatocracy, where hyper centers are privately owned by Facebook, Amazon, Google, Apple, Microsoft, et al., it is of little surprise that the tremendous energy consumed within these vast infrastructures is kept deliberately obscure. [3]
In 2010 there was a broad consensus that worldwide, data centers consumed approximately 194 TWh (terawatt-hours of electricity) of energy, representing about 1% of total demand. This is on par with the entire energy consumption of Iran that same year. [Source] In 2017, the EIA repeated this number for the year 2014: “Data centres worldwide consumed around 194 terawatt hours (TWh) of electricity in 2014, or about 1% of total demand. Although data centre workload is forecast to triple by 2020, related energy demand is expected to grow by only 3% thanks to continued efficiency gains.” In 2018, the figure for global energy consumption by data centers was said to have increased to 205 TWh. [“A 6% rise in power use with data-center computing growing by 550%”] [Source]
Today we can reflect on the past decade. Data centers have undergone “a ten-fold increase in traffic with a 25-fold jump in worldwide storage.” [Source] Yet, in 2020, data center consumption continues to be largely cited as approximately 200 TWh per year – (1% of global electricity consumption).
In 2011 Emerson Network Power stated that there were 509,147 data centers worldwide, taking up 285.8 million square feet of space – the equivalent of 5,955 football fields.
Again, reflect upon the annual cited consumption of data centers over the ten year time frame: 194 TWh in 2010, and ten years later, in 2020, 200 TWh. The estimate of 1% global energy consumption is referred to for both 2010 and 2020 – despite adding, roughly, 7.5 million data centres.
The 200 TWh of energy consumption per year claim (that remains flat) claim is further challenged by the European Union’s own research that concluded European data centers consumed 130 TWh in 2017, a 25% increase from 2014 (104 TWh), while Greenpeace reported China’s data industry to amount to 160 TWh in 2018. Together, these two figures alone suggest an annual total of 290 TWh. [Source] Further, consider that the consumption does not remain flat in the EU, despite having the newest, therefore most efficient, data centers.
In 2015, Siemens reported the global power demand for data centers as 416.2 TWh (far exceeding the UK’s total consumption, approximately 300 TWh).
Adding an additional 100 TWh to the 290 TWh cited above (the EU and China), in 2016, a Berkeley laboratory report for the US government estimated that the country’s data centres could require over 100 TWh of electricity a year by 2020, the rough equivalent of 10 large nuclear power stations. [Source] In 2017, data centers in the US alone used more than 90 TWh, the rough equivalent of 34 coal-powered plants generating 500 megawatts of power each. [Source]
2015 graphic, Siemens
In 2017, Hewlett Packard cites the energy consumption by data centers worldwide at 400 TWh:
2017 Hewlett Packard Presentation [Source]
While in 2018, “Nature”, Bloomberg, IEA, etc., continued to promote 200 TWh.
On January 6, 2020, the Uptime Institute assessed the global consumption of data centers as high as 500 TWh per annum. [Bashroush & Lawrence, 2020]. For some added perspective, 500 TWh is the equivalent of 50 large nuclear power stations:
“It seems likely that the annual consumption of energy by data centers is somewhere between 400 terawatt-hours (TWh) and 500 TWh, depending on what is counted as a data center. To put things in perspective in terms of demand, research by Uptime Institute Intelligence shows that every time an image is posted on Instagram by the Portuguese soccer star Cristiano Ronaldo (who at the time of writing has the highest number of followers on the platform), his more than 195 million followers consume nearly 30 megawatt-hours (MWh) of energy to view it.”
— Beyond PUE: Tackling IT’s wasted terawatts, Uptime Institute Intelligence report, Jan 6, 2020
The most dire assessments on the growing magnitude of energy consumed by communications technology and data centers comes from Anders Andrae, senior researcher at Huawei Technologies in Sweden. At the October 2017 Nordic Digital Business Summit Andrae forecast that communications technology may account for more than 20 percent of global energy consumption (20.7%) by 2025, accounting for 5.5% of the world’s total carbon emissions. These numbers represented the expected case scenario taking into account future energy efficiencies.
In respect to growing the exponential growth of data centers, Andrae cautions that data center energy consumption could increase a staggering 15-fold by 2030, amounting to roughly 11% of the global demand.
!["The share of ICT of global electricity usage: 2015 to 2025 with and without high global energy efficiency gains" [p. 18, Andrae, Anders, 2017/10/05, Total Consumer Power Consumption Forecast]](http://www.wrongkindofgreen.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/2017-Andrae-CT-of-Global-Share-690x617.png)
“The share of ICT of global electricity usage: 2015 to 2025 with and without high global energy efficiency gains” [p. 18, Andrae, Anders, 2017/10/05, Total Consumer Power Consumption Forecast]
In Andrae’s worst-case scenario, it is suggested that communication technologies could use as much as 51% of global electricity in 2030. In this scenario, “CT [communication technologies] electricity usage could contribute up to 23% of the globally released greenhouse gas emissions in 2030”.
[Annual electricity efficiency (EE) improvements were calculated at 15% (best), 10% (expected), and 5% (worst). From 2022, for EE only, 5% is assumed possible for all scenarios as the authors expect it will become more difficult to improve the electricity efficiency via Moore’s Law.] [p. 28, Andrae, A.S.G.; Edler, T. On Global Electricity Usage of Communication Technology: Trends to 2030. Challenges 2015, 6, 117-157.]
“The results shown in Figure 9c imply that the data centers and FAN [Fixed Access Networks] could drive a staggering 66% of the global CT electricity use in 2030, with fixed access Wi-Fi 15% and data centers 26%.” [p. 24, Andrae, A.S.G.; Edler, T. On Global Electricity Usage of Communication Technology: Trends to 2030. Challenges 2015, 6, 117-157.]
![Figure 8. "Share of communication technology of global electricity usage 2010–2030 As shown in Figure 8 [], the share of CT Sectors, depending on scenario, in 2010 is 8%–14%, in 2020 6%–21% and in 2030 8%–51%, respectively.' [p. 22, Andrae, A.S.G.; Edler, T. On Global Electricity Usage of Communication Technology: Trends to 2030. Challenges 2015, 6, 117-157.]](http://www.wrongkindofgreen.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Andrae-Global-Share-51-Percent-690x604.png)
Figure 8. “Share of communication technology of global electricity usage 2010–2030 As shown in Figure 8 [], the share of CT Sectors, depending on scenario, in 2010 is 8%–14%, in 2020 6%–21% and in 2030 8%–51%, respectively.’ [p. 22, Andrae, A.S.G.; Edler, T. On Global Electricity Usage of Communication Technology: Trends to 2030. Challenges 2015, 6, 117-157.]
![[p. 21, The share of different sections of ICT of global electricity use in 2015 and 2025, Andrae, Anders, 2017/10/05, Total Consumer Power Consumption Forecast]](http://www.wrongkindofgreen.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Andrae-ICT-Global-Electricity-Best-Case-2025-690x445.png)
[p. 21, The share of different sections of ICT of global electricity use in 2015 and 2025, Andrae, Anders, 2017/10/05, Total Consumer Power Consumption Forecast]
In regard to the Internet of Things, Andrae suggests that billions of internet-connected devices alone could produce 3.5% of global emissions within a ten year timeline, growing to 14% of global emissions by 2040. [Source]
And as bleak as these scenarios are (with even the best case scenarios projecting substantial increases in emissions) – the overall situation is much worse for one simple reason: the authors’ reliance on renewable energies as a means of mitigating overall impact (damage):
“However, until 2030, globally-generated renewable electricity is likely to exceed the electricity demand of all networks and data centers.” [Abstract, On Global Electricity Usage of Communication Technology: Trends to 2030]
“We believe that CT driven optimization of the electricity systems is a strong trend and a prerequisite for renewable power sources.” [p. 17, On Global Electricity Usage of Communication Technology: Trends to 2030]
“However, the trend of using renewable power is strong [157,158] and likely many data centers can be run GHG efficient, even if they do not find ways to reduce the absolute electricity usage.” [p. 17, On Global Electricity Usage of Communication Technology: Trends to 2030]
“To mitigate the worst-case scenario for climate change related to CT, the challenges related to introducing renewable electricity need to be overcome.” [p. 27, On Global Electricity Usage of Communication Technology: Trends to 2030]
“It seems though that planned power saving measures and innovation will be able to keep the electricity consumption of ICT and the World under control.” [p. 25, 2017, Total Consumer Power Consumption Forecast]
“Despite evident risks, it seems though that planned power saving measures and innovation will be able to keep the electricity consumption of ICT and the World under some kind of control.” [p. 2, 2019, Projecting the chiaroscuro of the electricity use of communication and computing from 2018 to 2030]
Yet, when one acknowledges the reality that industrial scale renewable energy is not sustainable – a key premise in modelling the ecological impacts of data centers (minimizing impact) – all such assumptions go straight out the window.
Here we can add that Andrae predicted that data centers on their own could produce 1.9Gt (or 3.2% of the global total) of carbon emissions by 2025. [Source] The DXC Technology white paper published in November, 2016 [Data centers play key role in Reducing GHG emissions] estimated that while consuming approx. 3 percent of global electricity, data centers worldwide already accounted for approximately 2% of total GHG emissions:
“Worldwide, it is estimated that data centers consume about 3 percent of the global electric supply and account for about 2 percent of total GHG emissions. That’s about the same as the entire airline industry. Producing electricity consumed by data centers will result in the release of 100 million metric tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) by 2020, according to the Natural Resources Defense Council.” [Source]
What becomes lost in discussion, amidst a declared planetary emergency, is the fact that we are adding exponentially to our energy consumption, cancelling out any real emission reductions. The massive growth of data centers that began in the US is now standard in Europe, with hyperscale data centers now expanding into South Asia where average year round temperatures for the humid region hover around 27 degrees Celsius. All while according to studies, approx. 40 percent of the total energy that data centers consume is due to the sensitive cooling [4] requirements of IT technologies. July 9, 2019: “With a projected compound annual growth rate of 13 percent, APAC [Asia Pacific] could eventually surpass the United States and European market.” [Source] In South Asia, a region of deep poverty where 20% of the world’s population reside, 2017 research suggests “that by the end of this century climate change could lead to summer heat waves with levels of heat and humidity that exceed what humans can survive without protection.” [Source]
At the May 2018 Around the World Conference in Canada, Andrae reiterated that ICT infrastructure cannot slow its overall electricity use by 2025, even with most optimistic improvements in data center and network technology. In 2019, Andrae increased his projection: “ICT infrastructure cannot slow its overall electricity use until 2030 and it will use several times more TWh than today. [p. 3, Projecting the chiaroscuro of the electricity use of communication and computing from 2018 to 2030, February, 2019]
Based on the aforementioned information (in addition to that which follows), it is safe to suggest that the energy consumed by data centers worldwide today is an extremely conservative 400-600 TWh – in line with 3-4% of all electricity produced on the planet – and far exceeding the greenhouse gas emissions produced by aviation.
In February 2019, Andrae published an update of his calculations and forecasts presented in 2015. In this study Andrae suggests we may see an increase in the energy demand of data centers worldwide to 1,929 TWh by 2030. For this calculation, Andrae calculated the global energy consumption of data centres in 2018 at 211 TWh. [Andrae, Anders, 2019/02/28, Predictions on the way to 2030 of internet’s electricity use]
On January 2020, CBC News reported that Andrae now expects that the world’s data centers alone will account for a colossal 651 TWh of electricity in the next year:
“Anders Andrae, a researcher at Huawei Technologies Sweden whose estimates are often cited, told CBC News in an email he expects the world’s data centres alone will devour up to 651 terawatt-hours of electricity in the next year. That’s nearly as much electricity as Canada’s entire energy sector produces. And it’s just the beginning.”
[Jan 2, 2020, ‘Completely unsustainable’: How streaming and other data demands take a toll on the environment] [International Journal of Green Technology, 2019, Comparison of Several Simplistic High-Level Approaches for Estimating the Global Energy and Electricity Use of ICT Networks and Data Centers, Anders S.G. Andrae]
In 2018, the total amount of electricity generated from the wind industry was 1 263 TWh, with the total from solar industry constituting 562 TWh. [5]
Corporate Damage Control – Hyperscale Greenwash
“We’ll also need vigorous development and deployment of emerging technologies — such as energy storage, advanced nuclear, and carbon capture and storage — that boost the availability of carbonfree energy around the clock.”
— Google: Moving toward 24×7 Carbon-Free Energy at Google Data Centers: Progress and Insights, Oct 2018
“Hyperscalers” such as Amazon, Google and Microsoft gloss over the growing concerns over their massive energy consumption by securing renewable-power purchase agreements. With unlimited budgets for public relations campaigns communication strategies, branding, and marketing, the corporate entities heavily publicize commitments to large-scale renewable energy initiatives. “net zero”, and “carbon negative” storytelling. Corporate press releases boast of commitments toward 100 percent renewable energy, as well as the promotion of investments in “*carbon free” energy sources. On September 19 2019, Google, which identifies itself as the “largest corporate buyer of renewable energy in the world”, announced they had made “the biggest corporate purchase of renewable energy in history”. These investments enable Google to declare it matches 100% of its global annual electricity consumption (for all global operations including data centers), through direct purchases of renewable energy. In layman’s terms – this is called offsetting – without mention of the word itself. It is nothing new and not nearly as exciting as Google would have you believe. Referred to as “CO2 colonialism” by indigenous peoples, offsetting is the means to privatize the skies and Earth’s forests while continuing to expand emissions.
[“Each Google facility is connected to its regional power grid just like any other electricity consumer; the power mix in each region usually includes some carbon-free resources (e.g. wind, solar, hydro, nuclear), but also carbon-based resources like coal, natural gas, and oil. * We define carbon-free energy as any type of electricity generation that does not directly emit carbon dioxide. This includes renewable like solar, wind, geothermal, hydropower, and biomass. Nuclear power is also carbon free. In the future, our framework can be extended to other technologies, such as carbon capture and storage, that are yet to be deployed at scale but could enable carbon-free power generation from additional sources.] [Source: Google: Moving toward 24×7 Carbon-Free Energy at Google Data Centers: Progress and Insights, October 2018]
Apple announced in 2018 that all of its facilities worldwide including its data centers are now powered by renewable energy. By saturating the public relations spin with never-ending references to wind and solar, this greenwash is made palatable to the liberal class – the non-profit industrial complex having successfully framed these two technologies as “clean”. The “carbon free” energy sources that do not make the headlines are those most sought by the corporate sector: biomass, nuclear, and capture carbon and storage (CCS).
“Amazon committed to achieve “net zero” emissions by 2040, which means it would need to offset any remaining emissions from its operations through investments in carbon removal projects… Amazon is following in the footsteps of another Seattle-area tech behemoth. Earlier this year, Microsoft announced it would spend $1 billion on “carbon reduction, capture, and removal technologies,” as part of an effort to offset the software company’s emissions across its entire history.”
— June 23, 2020, Amazon creates a $2 billion climate fund, as it struggles to cut its own emissions
And despite the fact that “renewable energy” is neither “clean”, nor “green”, nor “emissions free”, as marketed, on September 18 2019, Fortune reported “only 12 percent of Amazon’s Loudoun County data centers and 4.0 percent of Google’s are powered by renewable energy, despite their promise to shift to 100 percent renewable energy”.
Amazon owns nearly half of the cloud market. In July, 2019, it was reported that the annual revenues of Amazon Web Services, had grown to $15.5 billion in the global cloud infrastructure market with revenues of $32.4 billion. Data center industry leaders recognize Amazon Web Services (AWS) as “the invisible foundation of much of the internet.” Microsoft sits at second place, with 15% of the market share. [Source] This same week, Amazon launched a network of new data centers situated in Bahrain, increasing what Amazon cites as “availability zones” to 69 zones across 22 geographic regions, with plans to build nine new zones in Indonesia, Italy and South Africa. Today, Amazon Web Services spans “77 availability zones within 24 geographic regions around the world, and has announced plans for 15 more Availability Zones and 5 more AWS Regions in India, Indonesia, Japan, Spain, and Switzerland.” [Source] Amazon founder, Jeff Bezos, is a co-founder of Breakthrough Energy, launched in 2015 (alongside Mission Innovation at COP21 in Paris), with a keen focus on both nuclear and carbon capture and storage technology now being marketed to the public (a key aspect of expanding data center energy consumption). Between March and October, 2020, during the said pandemic, US billionaires saw their “net worth” rise by almost $1 trillion with Bezos on top with a net worth of approx. 200 billion USD. Here we can infer, that the person whose corporation now leads in mass global land degradation, resource use, energy consumption and subsequent greenhouse gas emissions, is also the wealthiest. All while Amazon continues to exploit its workers. All while those in the Global South face literal starvation. This is your new “stakeholder capitalism” as touted by World Economic Forum et al.
On September 14, 2020, Google released its most asinine statement to date: “As of today, we have eliminated Google’s entire carbon legacy (covering all our operational emissions before we became carbon neutral in 2007) through the purchase of high-quality carbon offsets. This means that Google’s lifetime net carbon footprint is now zero. We’re pleased to be the first major company to get this done, today.”
Here we must note that “net zero” has nothing to do with zero emissions, that carbon offsets, an instrument of imperialism and colonialism, do nothing to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions – and that Amazon Founder Jeff Bezos, Facebook founder Mark Zuckerberg, Microsoft founder Bill Gates, are all co-founders of the Breakthrough Energy Coalition (launched in 2015), which houses a $1 billion energy venture fund. Other co-founders of the coalition include aforementioned Jack Ma, and Marc Benioff. Breakthrough’s Mission Innovation, with its focus on nuclear, has partnered with 24 member states in addition to the EU.
“The [Google] white paper also highlights other technologies that could help bridge the gap between renewable power’s inherent intermittency and the consistent needs of its facilities, including “advanced nuclear, enhanced geothermal, low-impact hydro, long-duration storage, green hydrogen, and carbon capture and storage.” These are the same list of technologies that utilities, states and countries with zero-carbon commitments are planning to rely on to reach their goals.”
— Sept 14, 2020, Google Pledges 24/7 Carbon-Free Energy by 2030 [Emphasis added]
More to the point – even if renewable energies at scale were in fact a solution (which they are not), effectively replacing fossil fuel energies and lowering greenhouse gas emissions – this newly produced energy is effectively being devoured by the ICT sector. Here we witness the Jevons paradox; the easier it is to consume the product, the greater the increase in consumption. In 2019, coal was the world’s largest source of electricity, representing 35.18% of the total (despite a 3% year-on-year fall), followed by natural gas (23.52%), hydro (16.54%), nuclear (10.52%), wind (5.44%), other fossil fuels (3.47%). Solar accounted for 2.71%, biomass and waste accounted for 2.24%, with “other renewable” coming in at 0.4%. [Source]
Damage Control by the Non-Profit Industrial Complex
Academia, propped up by media – financed and owned by the ruling class – reacts swiftly in such instances. They are aided by those that worship at the altar of capital. [6] A broad consensus is formed that the growing trepidation surrounding exponential energy use and greenhouse gas emissions – corresponding with an exponential growth of data centers – is unfounded. To counter the concerns they cite rapid efficiency gains, and growth in renewable energies at scale (being built into the assumptions). The more the information generates concern, the greater the response by the gatekeepers. In this particular instance the issue is quickly reframed, utilizing the argument that the massive uptake in energy consumption will result in future efficiencies, or, that the growth is countered by rapid increased efficiencies, adding that cloud providers (such as Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Salesforce, etc.) are rapidly moving to zero emissions sources. A 2008 report produced by the World Wildlife Fund is an example of one such paper cited as a response to Andrae’s bleak assessment: ” A report [May 2008] from the World Wildlife Fund estimated that by 2030 efficiencies from smart devices and systems can potentially reduce CO2 emissions by as much as 8 gigatons, a figure approaching one quarter of total global emissions in 2018.” Here it can be noted that the World Wildlife Fund, which bears responsibility for the displacement and torture of Indigenous and tribal peoples (see the work of Survival International), is leading the charge to financialize nature in partnership with the World Economic Forum and other conservation NGOs.
“One has to search very hard to find a truthful statement from WWF. Lies have become their stock in trade.”
—conservation ecologist Dr. Mordecai Ogada
“The drivers for more energy use are simply too great to be offset by efficiency gains.”
— Jan 2020, Data center energy use goes up and up and up
The “decoupling” of growth and greenhouse gas emissions has become the preferred method of storytelling by global institutions such as UN-WEF et al., reverberated by those serving capital.
Another prime example is the public relations effort at Ericson: “Ericson, ICT and the climate – Have you ever worried how your online activities impact the climate? According to this report, the true impact may be a lot smaller than you think. [Source] The ICT sector’s carbon footprint could be reduced by over 80 percent if all electricity consumed came from renewable energy sources. [p. 3] 50 years – For the carbon emissions of a person making a transatlantic return flight, a smartphone could be used for over 50 years.” [p. 5] [A quick guide to your digital carbon footprint Deconstructing Information and Communication Technology’s carbon emissions, February 2020] In theory, that a smartphone (of obsolete design) could be used for over 50 years, is perhaps true – yet in reality, Westerners with money (and more importantly, access to debt), replace their smartphones with a new one every two years on average.
In addition to the magic trick of 7.5 million data centers coming online – with little to no added impact to global energy consumption or greenhouse gas emissions, is the complete omission of embodied energies and vast “natural resources” (biological communities) extracted (plundered) for the infrastructure. The stunning growth of the data center industry and its increasing demand for energy presents a stark ecological cost to our natural world – with ecosystems already collapsing due to the effects of industrial civilization, driven by the capitalist economic system. It is a tragic irony that this acceleration commences alongside alarm over climate change and protection of biodiversity feigned by the ruling class and industry.
[Source of graphic: Estimating a Data Center’s Electrical Carbon Footprint, White Paper 66, 2010. Note the 10-year life cycle of the data center itself.]
Woke Imperialism
If one considers that the production phase of a smartphone represents 90% of the direct energy consumption – we can safely assume the production required for hyperscale data center technologies, and subsequent impacts of such, are gargantuan.
The “green economy” can only flourish on the foundation of imperialism. Electronic devices are made from rare metals and rare earth elements which can only be extracted and refined using vast amounts of energy. More often than not, these are water-intensive processes. In the process of resource theft, it is those most vulnerable and impoverished who mine the required metals – in countries kept deliberately, and permanently, destabilized by foreign corporate interests and colonial states. Such destabilization and foreign interference will persist until the targeted state becomes depleted of the resource. In addition, land, forests and water become barren toxic wastelands, poisoning all life and the biosphere itself. The “great reset” of the global economy is the rebooting of imperialism and colonization of the Global South.
Add to this the fact that the Fourth Industrial Revolution architecture, built upon, dependent upon, 5G and 6G communication internet technologies, may very well require more metals than the Earth can provide. As a result, industry has already begun its pursuit of yet another emerging market – seabed mining, at scale.
And as oligarchs forge ahead with their plans to mine the planet’s oceans as the next terrain for industrial plunder, global tech giants have yet another vision of what the full colonization of oceans may entail. On September 14, 2020 Microsoft announced “underwater data centers are a go” after its researchers retrieved the prototype sealed capsule of a data center, off the shores of Orkney Islands, Scotland, where it had been submerged in the spring of 2018. [Source] The experiment, Project Natick was the second carried out by Microsoft. The first capsule was submerged off the California coast in 2014.
Energy intensive recycling, on almost every level, has proven to be a spectacular failure – and yet it has morphed into another trillion dollar industry. For this reason, storytelling, to convince the citizenry to believe that recycling will be a key component of mitigating environmental impacts and destruction going forward, will persist.
Added to the aforementioned issues, to which we are collectively blind, or perhaps oblivious to, is the obsolescence by design. In most cases, the life span of a data center is typically 10 years at best. Hyperscale data centers are expected to last between 15 and 20 years. These short life spans are still out of sync with the far faster pace of the internet technologies (IT) that comprise the centers with a vast amount of the components being replaced at a 2-5 year refresh cycle: “Hyperscalers use IT equipment for only a few initial years of its much longer useful life, and for them that’s it. It’s onto the next best CPU, or the next best storage technology.”[Source]
In addition to this accelerating nightmare, coolants for data centers require toxic/hazardous chemicals, while large diesel generators are required for power shortages and outages. Consider that the Apple data center which was planned for Athenry, Co. Galway, Ireland, but scrapped in 2018 would have required 144 large diesel generators as back-up for when there was no wind, or insufficient renewable energy production, to support the power demands. [Source] In addition to diesel generators, battery (lead acid) back-ups are required for power shortages. This leads to another nightmare, now unfolding.
Lithium.
Here we must take into account, the escalating global tensions as power shifts to China. Rare earth metals and minerals are coveted by the world’s most powerful states. Access to these geographical regions, where the metals and minerals are found in abundance, is today a non-negotiable imperative for imperial governments and the transnational corporations they serve.
“A 2018 Bloomberg New Energy Finance report forecasted that Li-ion technology will comprise 40 percent of all data centre backup batteries by 2025, and that in the hyperscale sector, Li-ion will become the predominant battery technology, accounting for 55 percent of UPS [Uninterruptible Power Supply] batteries.” [October 23, 2019]
January 11. 2020: “The uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is the cornerstone of the modern data centre, and is one of the primary culprits of inefficient usage of hardware. Traditional lead-based batteries are becoming increasingly redundant… Huawei’s SmartLi UPS solution answers the call by leveraging the company’s cutting-edge Li-ion battery technology and delivering a ‘reinvention’ of the power supply system for the next generation of data centres… Reliability is further enshrined within the product with its 10-year, 5,000 cycle lifetime.” [Source: The importance of the lithium-ion battery for future data centers]
No further do we need to look, to see the “green energy transition”, as imperialism, quantified, than the November 11, 2019 coup in Bolivia, a country holding vast reserves of Earth’s lithium. (The single largest lithium deposit in the Salar de Uyuni, a salt pan, is so massive, it can be seen from space.)
On July, 25, 2020, billionaire and SpaceX founder Elon Musk responded to a comment directed toward him on Twitter. The comment read: “You know what wasn’t in the best interest of people? The U.S. government organizing a coup against Evo Morales in Bolivia so you could obtain the lithium there.” Musk responded with “We will coup whoever we want! Deal with it.” Evo Morales, the first Indigenous president of Bolivia, overthrown in a coup, responded to Musk, drawing attention to the massacres that resulted from the coup, with a reminder of the Bolivian peoples’ sovereignty and self-determination: “We will always defend our resources!” That Musk is a grotesque human being, yet celebrated in our rapidly devolving Western culture, as a person to be both worshipped and emulated, speaks to our declining ability to even recognize the world’s problems, much less solve them. The Western worldview, which Musk et al. espouse, is founded on white supremacist ideology, an ideology shared by a large component of those that identify as liberal or progressive. Subjected to centuries of conditioning, generation after generation, this racist ideology hums beneath the global, capitalist economic system. A conditioned populace no longer recognizes it.
Further, the global race toward blockchain technology, dependent on the colossal expansion of militarized 5G networks, has already begun. On April 25, 2020, China launched the world’s largest Blockchain network (BSN) as the country rapidly transitions to digital central bank currency, digital wallets, digital identifications, automation, IoT, AI and biometrics at scale. On August 10, 2020, China rolled out its international website with Google and Amazon Web Services listed as cloud service providers. This vast lead in central bank digital currency (CBDC), digitalization and 4IR technologies, is recognized as a major security threat to the US. [Source]
Data centers are the heat engines of the internet. Eight million running 24/7 in order to meet the global demand. A demand now set to expand exponentially under Fourth Industrial Revolution digitalization. The more data produced – the more the storage infrastructures must expand. This growth will be unprecedented.
Here we can momentarily contemplate the World Economic Forum’s stakeholder capitalism storytelling, best described as a public relations rebranding exercise. Data centers are proliferating, while approximately 1 billion people, after 270 years of industrial revolutions, still have no access to electricity.
5G as Catalyst for Voracious Energy Consumption
The IEA forecasts that data and digital services will result in global internet traffic doubling by 2022. Internet of Things (IoT) connections (“a prevalent system in which people, processes, data, and things connect to the Internet and each other”, Cisco), will triple from 9.1 billion in 2018 to 25 billion in 2025, while global IoT revenue will quadruple to $1.1 trillion (a fourfold increase from 2018). The exponential growth of these devices is driven by “intentional obsolescence”. Mobile subscribers are projected to approach 6 billion by 2025. A projected 79% of all internet users will use smartphones exclusively to access content (up from 60% in 2018). [“In the most advanced countries, today’s digital consumers (using PCs and smartphones) will likely become tomorrow’s augmented customers, adopting emerging technologies such as AI (via smart speakers) and immersive reality.”] [Source: The Mobile Economy 2019, GSMA Intelligence] The exponential growth of digitalization [7], coupled with rapid growth of smartphone and social media users in Asia Pacific, followed by Africa, will drive unprecedented exponential growth in data center and network services.
According to Cisco, 60% of the world’s population will be online by 2022. But that was predicted in 2018 – prior to the COVID-19 “great reset”. By June 11, 2020, online access had reached 53% (Klaus Schwab), and in July 2020 the number of global internet users worldwide was reported as having reached 59% (Statista). That’s a full two years ahead of schedule.
“ICT systems give a non-negligible contribution to world electricity consumption and carbon dioxide (CO 2) footprint. This contribution will sustain since the increased demand for user’ s connectivity and an explosion of traffic volumes necessitate continuous expansion of current ICTs services and deployment of new infrastructures and technologies.”
— November 8, 2019, Greener, Energy-Efficient and Sustainable Networks: State-Of-The-Art and New Trends
Of particular concern is the rapid growth of streaming video and gaming. By 2022 traffic from internet video is projected to have doubled from 2019, with online gaming projected to quadruple – amounting to 87% of consumer internet traffic by 2022. [Source] In addition to this dismal reality, emerging fourth industrial revolution technologies (5G, blockchain, virtual reality) will place further demands on our energy consumption, our natural world, and our collective well-being. While reading and contemplating these analyses and resulting data, it is important to bear in mind that these were compiled prior to “COVID-19, The Great Reset“. Recall Schwab, on June 11, 2020, proudly sharing the fact that some video streaming services have already grown twenty fold during this “watershed moment”.
“As blockchain applications become more widespread, understanding and managing their energy-use implications may become increasingly important for energy analysts and policy makers.”
— Data Centres and Data Transmission Networks, On track, International Energy Agency, June 1, 2020
Graph: “A recent IDC study claims that by 2025, worldwide data traffic will have grown by 61 percent to 175 zettabytes, with roughly 75 percent of the population having at least one data interaction every 18 seconds.” [Source]
The energy intensive 5G cellular networks serve as the very foundation of the new global architecture, as designed and sought by the ruling class. ICT experts suggest that “thanks to a combination of massive MIMO antennas, legacy networks in multiple bands and the massive proliferation of small cells”, 5G networks will consume three and half times more electricity as present 4G networks. [Source, October 30, 2019] A more recent report by ABI Research forecasts 5G energy consumption to increase by a magnitude of 61 times by the end of this decade:
“By 2028, 5G is expected to overtake LTE [Long-Term Evolution]. By this stage, both 5G NR Radio Access Network (RAN) and SA core network will be fully commercialized. As such, 5G energy consumption is expected to increase by 61x from 2020 to 2030.”
— September, 2020, ABI Research, Environmentally Sustainable 5G Deployment: Energy Consumption Analysis and Best Practices
As a tool for deployment of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the World Economic Forum seeks social license by leveraging the biodiversity crisis (caused by these very people, entities and institutions) as a means to obtaining social licence. That feigned concern for the ecology of the planet, and health of all life, quickly reveals itself when one becomes aware of the environmental threats that come with 5G, as well as the associated health risks, to all life forms. Although 403 scientists and doctors (as of September 23, 2020) across the European Union have signed a declaration calling for all 5G roll-out plans to be stopped, such appeals to the EU, and the World Health Organization, have been met with silence. “Listen to the science” and “unite behind the science”, but only when the science serves capital. The 2018 emerging risks report, from the European Commission’s SCHEER (Scientific Committee on Health, Environmental and Emerging Risks) committee calls attention to the potential effects on wildlife due to increases of electromagnetic radiation.
Worse, but par for the course, those tasked with protecting capital, in servitude to the hand that feeds, have deliberately framed very real 5G concerns as “conspiracy theory“, in a calculated effort to roll out 5G with as little dissent as possible.
“The overall energy and emission impacts of 5G are still uncertain.”
— Data Centres and Data Transmission Networks, On track, International Energy Agency, June 1, 2020
“The data streamed by an autonomous car would completely fill an average laptop’s 240GB hard drive in less than a minute.” [Source]
“5G will prompt Energy Consumption to Grow by staggering 160% in 10 years” [Source]
Automation at scale, artificial intelligence (AI)/machine learning, 3D printing, blockchain, crypto currencies, autonomous vehicles, virtual and augmented reality, Internet of Things (IoT), Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), precision agriculture, gene editing, robotics, “smart” cities: the list is endless and ever expanding as the world’s most powerful technocrats lead the transition from bricks to mortar, to an online, digitalized fourth industrial revolution education for our children, fourth industrial revolution healthcare (ehealth, digital medicine) and an automated global workforce. With this digitalization, comes the merger of human with machine: augmentation and neuro-technological brain enhancements. Cybersecurity will be the battle space of the 21st century. Emerging technologies that drive militarism, including Lethal Autonomous Weapons Systems (LAWS), drone targeting, and hypersonic weapons are predicted to become the norm, further dividing and destroying.
“Tesla Chief Executive Elon Musk said on Tuesday that electricity consumption will double if the world’s car fleets are electrified, increasing the need to expand nuclear, solar, geothermal and wind energy generating sources.” — Reuters [8]
A permissioned blockchain ‘ecosystem’ “is the key infrastructure-of-infrastructures that allows the vertical integration of cloud computing, 5G communications, industrial IOT, AI and big data, with fintech and other application-level services overlayed on the stack”. [Source] 5G broadband is the instrumental network that transports the data – with data centers as the heat engines. Together, they create a digital technosphere, purposely eroding our physical biosphere, coupled with a coming ecological nightmare which will be unprecedented in scale. All under the guise of climate mitigation and the protection of biodiversity.
The following is an excerpt from the article “The World in 2030. Hyper-connected and Hyper-fragmented”, authored by Mark Leonard, Director of the European Council on Foreign Relations, and past Chairman of the World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council on Geo-economics:
“Connectivity can cause conflict… Rather than creating a harmonious global village, we increasingly recognise that the very same forces that have brought people together and broken down boundaries between peoples and nations are leading to nationalism, protectionism, and a desire for control. The world of 2030 will therefore likely be more closely bound together than at any time in history, but also one where political fragmentation is at an all-time high. It will be a world in which connections between people and countries become instrumentalised and weaponised… The Digital Revolution has brought people together in a single connected web and is going to lead to further fragmentation of societies…
Migration and the movement of people will be weaponised and will also be the defining topic for politics, even more so than already now and both in countries which are scared for their existence due to demographic changes and countries that are experiencing migration influxes. Moreover, international law and institutions will grow increasingly weaponised: the idea of lawfare, using the norms and processes of these institutions to damage the opponent, is going to be a very well-known concept. We thought of law and institutions as a constraint on competition and a way of regulating our relations in the past. They will now become a core means and field for competition at the same time.” [Source]
To further demonstrate the illusory concern over the biodiversity crisis, being leveraged with COVID-19, by the World Economic Forum et al., as a means of ushering in the “great reset” as rapidly as possible, satellites are already being launched into space that will support the 5G and 6G networks, connecting trillions of devices. On November 11, 2019 SpaceX’s Starlink broadband network, owned by Elon Musk, rocketed 60 satellites into orbit. This followed a launch of 60 SpaceX satellites launched in May 2019. By February 2020, SpaceX had launched five batches of 60 Starlink satellites into orbit – with a long-term goal of 30,000.
But Musk is far from alone in his quest to dominate the sky. There are 57,000 satellites planned through 2029. “When there are 50,000 satellites in the sky, ‘you’ll see the sky crawling,’ says Tony Tyson, a University of California Davis astronomer and physicist. ‘Every square degree will have something crawling in it.'” In addition, unregulated rocket launch emissions will further impact the global atmosphere while adding enormous quantities of space debris. [Source] While “corona” serves to distract a global populace, a virus Klaus Schwab describes as “mild” in his book COVID-19 The Great Reset, one thing is clear – billionaires are the most dangerous virus of all.
“Soon, Earth may be blanketed by tens of thousands of satellites, and they’ll greatly outnumber the approximately 9,000 stars that are visible to an unaided human eye.”
— January 29, 2020, The night sky is increasingly dystopian
The absolute lack of regard for the subsequent harm that this will inflict upon nocturnal sentient animals and fauna is beyond pathological. The arrogance is blatant, astounding, and unequivocal. In addition to physiological harm, this new and unprecedented form of light pollution will disrupt navigation and migration patterns that have evolved within animals, birds, and insects, over millennia.”The rhythm of life is orchestrated by the natural diurnal patterns of light and dark, so disruption to these patterns impacts the ecological dynamics.” [The Hague]
The Dire Ecological Impacts & Consequences that Lie Ahead
Here it is imperative to note the consolidation of power happening in real time. World Economic Forum founder and CEO Klaus Schwab refers to this consolidation as a new global architecture; the new global governance. The following dates of are of paramount significance. On May 18, 2018, the World Bank partners with the United Nations. On June 13, 2019, the World Economic Forum partners with the United Nations. On March 11, 2020, the World Economic Forum partners with the World Health Organization (a UN body) launching the COVID Action Platform, a coalition of 200 of the world’s most powerful corporations. This number would quickly swell to over 700. On this same day, March 11, 2020, the WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic. The UN-WEF partnership firmly positions Word Economic Forum at the helm of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs, also referred to as the Global Goals), which they are frothing at the mouth to implement. This is not because they care about poverty, biodiversity, the climate, or world hunger. Marketed with holistic language, dressed with beautiful images of brown smiling children, SDGs represent the new poverty economy (impact investing/social impact bonds) and emerging markets. Children as human capital data to be commodified on blockchain linking behaviour to benefits. Coercion has been repackaged as empowerment. The human population to be controlled via digital identity systems tied to cashless benefit payments within the context of a militarized 5G, IoT, and an augmented reality environment. A world where every function of nature is monetized, to be bought, sold and traded on Wall Street.

“Around $6 trillion a year will need to be invested to deliver the SDGs, most of it in emerging markets.”
Fourth revolution technologies, in particular 5G and the ICT, fall under the SDG #9: “Build resilient infrastructure, promote sustainable industrialization and foster innovation”; 9c: “significantly increase access to ICT and strive to provide universal and affordable access to Internet in the LDCs (least-developed countries) by 2020”. These are central to the goals of the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO). A critical component toward the full implementation of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (“Industry 4.0”) is digitalization. In the EU, 4.0 digitalization is being rolled out under the EU Green Deal in service to Klaus Schwab.
“Around $6 trillion a year will need to be invested to deliver the SDGs, most of it in emerging markets.”
— At Last… Climate Consensus on the Magic Mountain, February 3, 2020, SYSTEMIQ
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is a term largely accredited to Schwab. He describes it as being “characterized by a fusion of technologies that is blurring the lines between the physical, digital and biological spheres.” The World Economic Forum website adds that it will impact “all disciplines, economies and industries, and even challenging ideas about what it means to be human.” [Source] One may question why collectively, we would accept an architecture that will further destroy the natural world – to become only further disconnected from our natural world. A world that will be further devastated by the very global architecture purported to save it.
“Once we can access people’s thoughts and people’s emotions, we have to create a space that enables people to think freely, to think divergent and creative thoughts. And in a society where people fear having those thoughts, the likihood of being able to enjoy progress is significantly diminished.” [The Fourth Industrial Revolution | Full Version, World Economic Forum, April 13, 2016]
“The very idea of humans being some sort of natural concept is really going to change. Our bodies will be so high–tech, we won’t be able to really distinguish between what is natural and what is artificial”
— The Fourth Industrial Revolution | Full Version, World Economic Forum, April 13, 2016
In closing this segment, we can juxtapose Andrae’s suggestion that communications technology may account for more than 20% of global energy consumption by 2025, with this observation articulated by The Guardian’s John Vidal back in 2017: “The industry has encouraged the idea that the digital transformation of economies and large scale energy efficiencies will slash global emissions by 20% or more.”
Thus, the power elite intend to crush the informal sectors and whole societies in the Global South – and across the world, in order to usher fourth industrial revolution digitalization, utilizing COVID-19 as the catalyst. Under the guise of protecting the biosphere and mitigating climate change, the “Great Reset”, decades in the making, has been foisted upon us by the ruling class. The new global architecture masks its intentions with illusory concern over ecological crises that they created. That they accelerate. To “slash global emissions by 20% or more” by rolling out an infrastructure that may well translate to 23% of all global emissions by 2030. At the cost of further plundering the Earth. At the cost of a growing, collective mental duress.

Imperative 21: Allies for System Change, a Virtual Convening of the Skoll World Forum – April 1, 2020
This depraved psychosis only makes sense when one understands that “action on climate” is not about mitigating climate change. Rather, it serves as an opportunity to “reset” capitalism as it teetered on the verge of collapse with global debt having reached a staggering 253 trillion dollars. [The global debt has since ballooned to a whopping 272 trillion dollars.] We are embarking on an inescapable and irreversible technological enslavement.
“Who survives? Amazon, Netflix, Google, Comcast, Facebook, et al. Those who control the screens control the world. It is a new morning in hell.”
— John Steppling, Morning in Hell, October 7, 2020
The more that states, industries, institutions, platforms and devices rely on data and internet interconnectivity to function, the more our global energy consumption will soar.
Assessing “the silicon footprint, [and the] environmental impact of hyperconnected technologies”, the Institute for the Future concludes, “These facts considered together increase the probability that the net environmental impact of a hyperconnected world will be negative.” [The Hyperconnected World of 2030–2040; made possible by the support of the Office of Director of National Intelligence; IFTF convened a team of technology experts and researchers to look at the future of the hyperconnected world in a day-long workshop in 2019.]
The ruling classes intend to assign monetary value to nature, global in scale. The monetization of “social and human capital” will follow. This would entail the greatest transformation to the economic system in modern history. “Natural capital” valuation is expected to replace GDP (Gross Domestic Product) with nature to be bought, sold and traded on Wall Street. This, coupled with “protected areas” that would further displace Indigenous peoples. In addition to data as the new oil, classifying nature as an asset class represents a global corporate coup of the commons. With capitalism having reached its limits, and physical labour now disposable, to be replaced by automation/robotics, data and nature represent new and untapped emerging markets. Utilizing the very real fact that nature is vital to all life, we are told to believe that it can only be valued properly by humans if monetized (i.e. “natural capital” and “payments for ecosystem services”). Yet consider this: In just a few months the World Health Organization (partnering with the World Economic Forum on March 13, 2020), and the United Nations (partnering with the World Economic Forum on June 11, 2019) – in unison with the sycophant institutions, academia, sciences, media and NGOs that serve them. et al. – effectively utilized cognitive sciences, psychology, conformity and fear, to convince an entire global population that masks must be worn in order to save lives. In this same way, if they truly desired to convince a population that it is critical to protect nature against development, industry, privatization, corporate capture and monetization – as nature is vital to all life, and should be respected as such, they could easily do so. They do not – because it is they, primarily, who are wholly responsible for the bulk of the plunder they wish to continue. The global decimation of nature, from which they build and retain their fortunes and status.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution has caused and will continue to cause mass upheaval, displacement, severe impacts, and untold suffering to the peasantry, Indigenous, working class and those belonging to the informal economy. The middle class will not be spared. Yet this depraved new global architecture, dangerous to life, human, sentient and biological, is pushed forward despite advanced knowledge of foretold tragedy – solely for the pursuit of money, profits and power. It is this very fact that shows us unequivocally and irrevocably that promises for a just transition, green deals, new deals, build back better schemes, are nothing but empty, hollow assurances, void of intent. These are the lies they tell. Promises and assertions that are nothing more than alibis.
Western and ruling class ideologies have played a crucial and cruel role in the violent transformation of the peoples, ecosystems and biosphere. The Fourth Industrial Revolution represents the most violent transformation of all. For as long as the ruling class is allowed to exist, social and environmental justice remain pipe dreams.
The ruling class has weaponized the power of both fear and conformity against us. That Covid-19 is the catalyst to usher in a new global architecture, that is the 4IR, is not conjecture, not “conspiracy theory“, but a fact. Full compliance is the goal. A physical transformation away from our physical world, towards a full embracing of an artificial, digital, virtual world, is being engineered, right before our very eyes. The social engineering of a collective consciousness. Social license is being harvested to reset the capitalist system – under the guise of a climate emergency and saving the planet. This we know: the planet will not be saved by those that have destroyed it.
End Notes:
[1] The September 11, 2020 article “The Social Dilemma Wants You to Delete Facebook”, is somewhat disingenuous, with the film’s emphasis on deleting notifications, rather than the social media platform. Yet what is of interest, and on the mark, is the reference to a TED Talk by Eli Pariser explaining “filter bubbles are the result of internet platforms’ race to feed users the information that will keep them coming back.” Pariser should know – as a co-founder of both Avaaz and Upworthy – with cofounder Chris Hughes of Facebook.
[2] “The sprawling camp, which is divided into 12 districts across 13 square kilometres, is surrounded by barbed wire and guarded by police and military. Refugees cannot leave without permission. If they want to move to a city elsewhere in the country, they need a Jordanian sponsor guaranteeing financial support – a condition that leaves many stuck in the camp.” [Source]
[3] Gov.UK: “We asked our hosting providers, Amazon Web Services, UKCloud and Carrenza, to tell us how much electricity we use, and how much CO2 we produce. Only one of our providers, UKCloud, agreed to give us data about our electricity usage. For Amazon and Carrenza, we made a guess about the amount of electricity we use, assuming a percentage of our monthly bill. In addition, neither Amazon nor Google currently shares information about how much CO2 their data centres produce.” [Source]
[4] “Researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, the International Energy Agency (IEA), and Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) have concluded that room air conditioners alone — the typical window and split units used in most homes — are set to account for over 130 gigatons (GT) of CO2 emissions between now and 2050. That would account for 20–40% of the world’s remaining “carbon budget” (the most we can emit while still keeping global warming to less than 2?C above pre-industrial levels — the goal set at the Paris Climate Conference in 2015).” [Source] “If room air conditioners have a massive emission, then it is hard to imagine the immense emissions that is occurring on the industrial scale.”
[5] In 2018, the total amount of electricity generated from renewables was 6 586 TWh. Renewable hydro accounted for about 63% of this (4 149 TWh), followed by wind energy (1 263 TWh), solar energy (562 TWh), bioenergy (523 TWh), geothermal energy (88 TWh) and marine energy (1 TWh). [Source: IRENA – Renewable energy highlights, July 1, 2020]
[6] “But data centers are rapidly becoming more energy efficient, and new research suggests there’s no longer a close link between more cloud computing and more energy use. A report published Thursday in Science credits the progress to better management, more efficient hardware and the rise of “hyperscale” data centers created by tech giants…The data-center industry’s 20% annual improvement in energy intensity dwarfs all other major parts of the economy. The power used today by data centers, 1% of the global total, is roughly the same as it was in 2010… This new research is the first major attempt to compile a bottom-up view of data-center energy use in a decade. Researchers based their work on reports published by Cisco Systems, Inc., Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and the International Energy Agency, among other sources.” [Source]
[7] The Cisco Annual Internet Report, 2018-2023 predicts that by 2023, there will be 299.1 billion global mobile application downloads, up from 194 billion global mobile application downloads in 2018. By 2023, there will be 29.3 billion global devices and connections (3.6 devices and connections per capita), up from 18.4 billion devices and connections in 2018 (2.4 devices and connections per capita). Similarly, Gartner forecasts that 14.2 billion connected things will be in use in 2019, and that the total will reach 25 billion by 2021, producing immense volume of data. [Source]
[8] Quote added on December 4, 2020 after initial publication. [Source] Full quote as follows: “Total electricity power consumption obviously will increase. I mean when everything, when all transport goes electric, or road transport going electric, it will approximately double the electricity usage, um total electricity usage. Like I said, because most of its at night, [charging batteries], that doesn’t mean a doubling of the power plant. But we will need to increase the amount of solar and wind, geothermal, hydro, [and] nuclear, I think is fine. Like I said, in order to solve the needs of electric vehicles.” — AxelSpringer Award Talk with Questions from other CEOs, December 1, 2020 [Source]
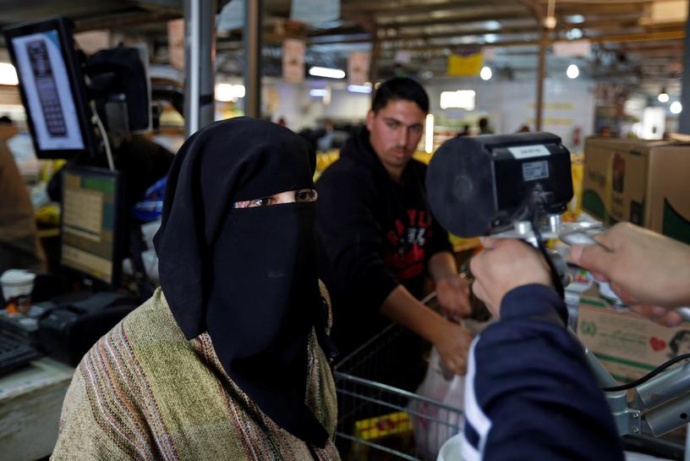
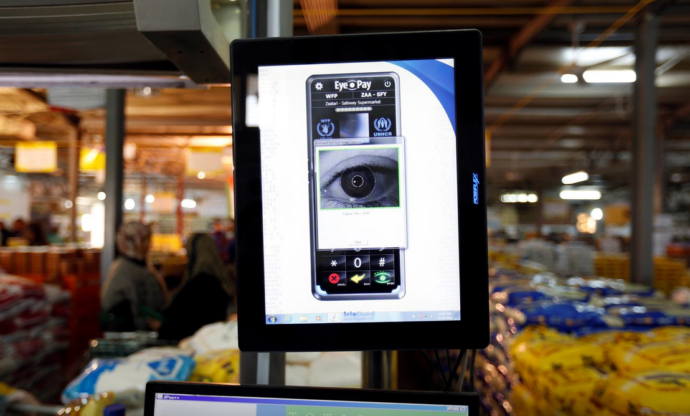

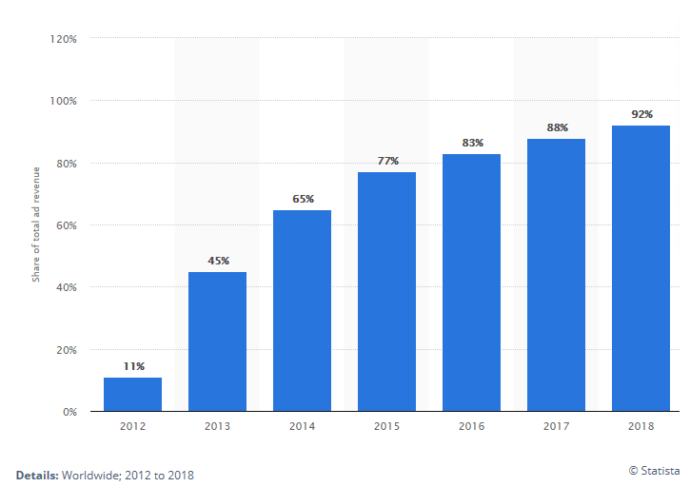






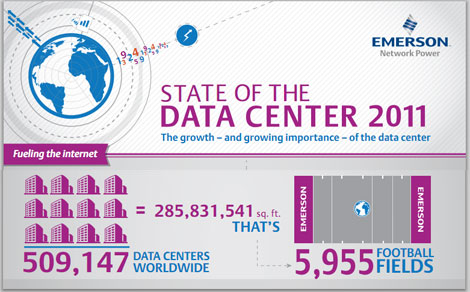
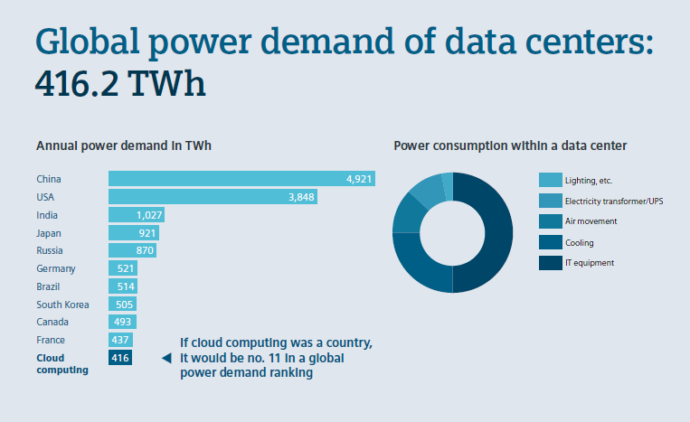
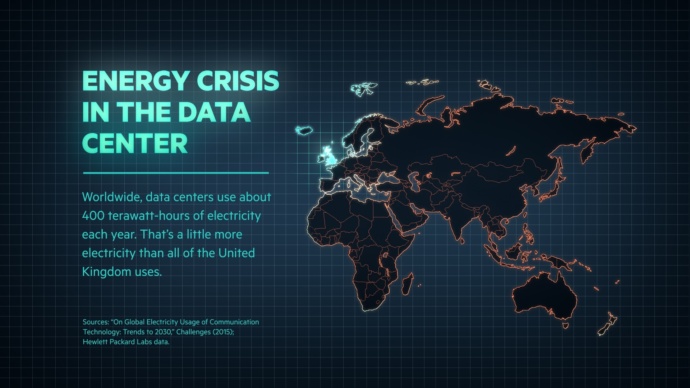
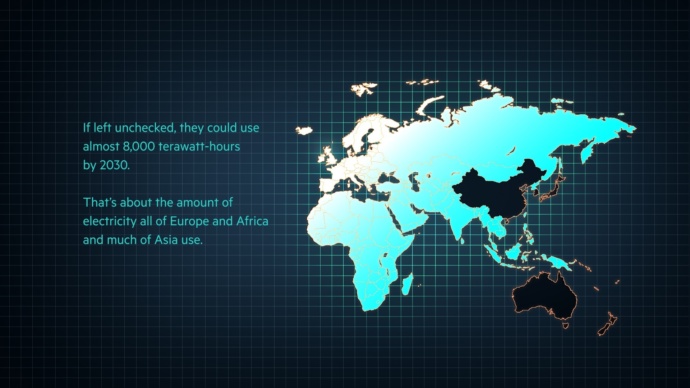
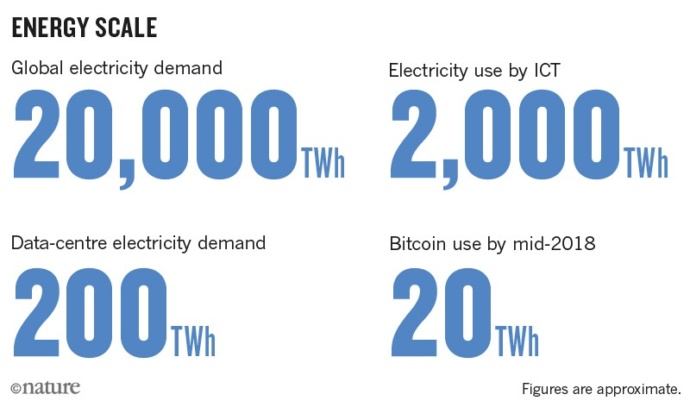
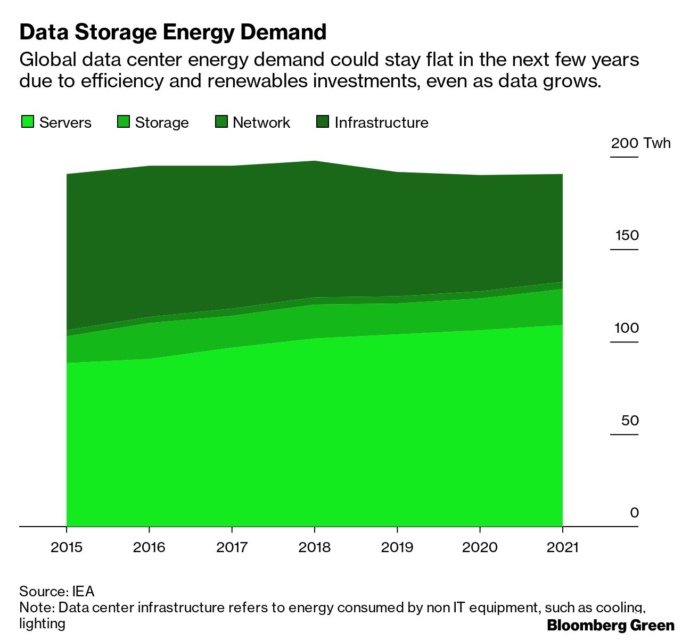


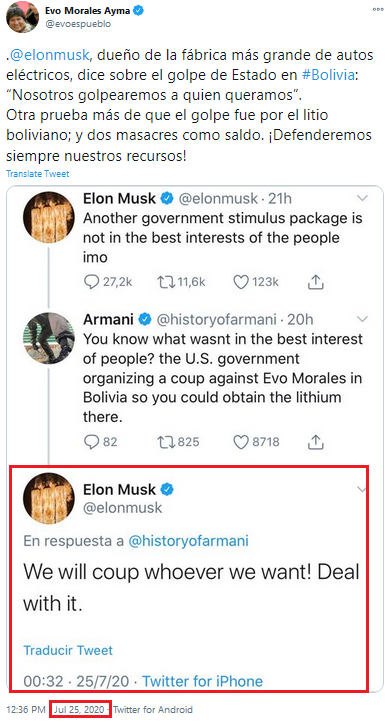
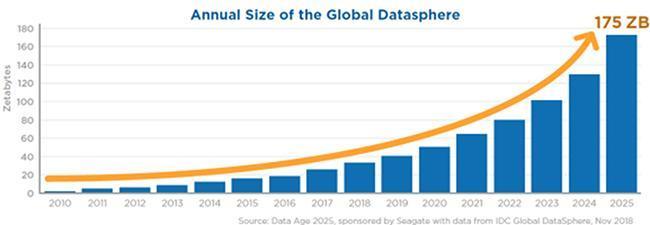

 Become a Patron!
Become a Patron!